The tooth fairy is a welcome guest for any child who has lost a tooth. Not only will the fairy leave a small gift under the child’s pillow, but they be assured of a replacement tooth in a few months. Unfortunately, the scenario is quite different for adults grappling with a loss of teeth. Luckily, there may be some hope thanks to a new study performed by scientists at Kyoto University and the University of Fukui.
A dental breakthrough
While the typical adult mouth houses 32 teeth, approximately 1% of the population exhibits variations of them, either possessing more or fewer teeth due to congenital conditions. Researchers have delved into the genetic factors behind cases of excessive teeth, seeking valuable insights into the potential regeneration of teeth in adults. This study is the first to show that monoclonal antibodies can help regrow teeth. It suggests a new way to treat a dental problem that currently requires implants and other artificial solutions.
A bit of science
The research team disclosed that an antibody targeting a specific gene, known as uterine sensitization-associated gene-1 (USAG-1), can induce tooth development in mice affected by tooth agenesis, a congenital condition. The findings were published in the journal, Science Advances.
As per Katsu Takahashi, a senior lecturer at the Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine and one of the principal contributors to the study, the essential molecules crucial for the development of teeth have already been pinpointed. “The morphogenesis of individual teeth depends on the interactions of several molecules including BMP, or bone morphogenetic protein, and Wnt signaling,” says Takahashi.
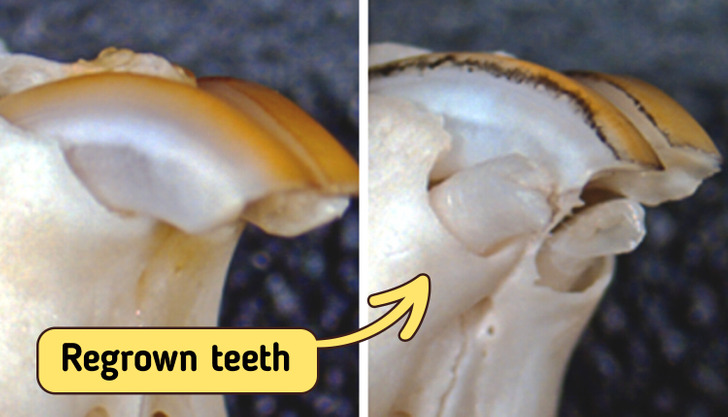
On April 13, 2021, the University of Kyoto posted its first pic of newly-grown teeth in mice.
BMP and Wnt are involved in more than just tooth development; they affect the growth of organs and tissues early in the body’s development. Because drugs affecting them directly might have broad side effects, scientists are cautious. To find a potentially safer method, researchers focused on the gene USAG-1, thinking that aiming at factors countering BMP and Wnt specifically in tooth development could be more precise.
“We knew that suppressing USAG-1 benefits tooth growth. What we did not know was whether it would be enough,” added Takahashi.
The first results
Scientists looked at how different monoclonal antibodies affect USAG-1. Monoclonal antibodies are often used to treat things like cancer and arthritis and for making vaccines. Tests with this antibody showed that BMP signaling is crucial for deciding the number of teeth in mice. Also, just one treatment was enough to grow a whole tooth. Further tests confirmed these positive results in ferrets too.
“Ferrets are diphyodont animals with similar dental patterns to humans. Our next plan is to test the antibodies on other animals, such as pigs and dogs,” explained Takahashi.
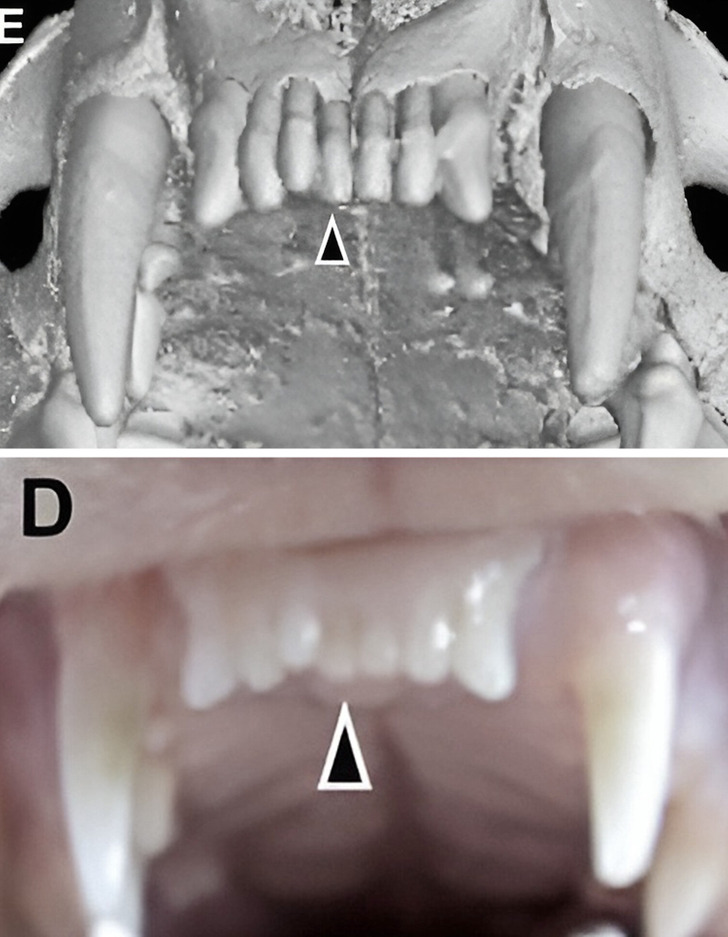
Fully regrown frontal teeth in ferrets
The next steps

Now, scientists are going to test the drug on healthy adults. If that goes well, the team plans to try it on kids aged 2 to 6 with a rare tooth problem called anodontia, a genetic disorder defined as the absence of all teeth. These kids will get one shot of the drug to see if it makes their teeth grow. If everything works out, the medicine might be approved by 2030.
Takahashi sees the new medicine as an additional choice for individuals who are missing some or all of their teeth.
“The idea of growing new teeth is every dentist’s dream,” Takahashi told the Japanese newspaper, The Mainichi in June this year. “I’ve been working on this since I was a graduate student. I was confident I’d be able to make it happen.”
So hopefully, by the year 2030, humans will get a chance to have their third generation of teeth grown and say goodbye to implants. Until then, make sure to keep your teeth strong and healthy — this article will help you with that.
Preview photo credit KyotoU_News / Twitter
Meu filho de 16 anos foi passar o verão com a avó – um dia, recebi uma ligação dela

Quando meu filho de 16 anos se ofereceu para passar o verão cuidando de sua avó deficiente, pensei que ele finalmente tinha virado a esquina. Mas uma noite, um telefonema assustador da minha mãe destruiu essa esperança.
“Por favor, venha me salvar dele!”, sussurrou a voz da minha mãe pelo telefone, quase sem fôlego.

Uma idosa assustada falando ao telefone | Fonte: Midjourney
Suas palavras eram cortantes de medo, um tom que eu nunca tinha ouvido dela. Meu estômago deu um nó. Antes que eu pudesse responder, a linha caiu.
Olhei para o meu telefone, descrença misturada com choque. Minha mãe forte e ferozmente independente estava assustada. E eu sabia exatamente quem “ele” era.

Uma mulher furiosa | Fonte: Pexels
Meu filho sempre foi um sujeito difícil de lidar, mas ultimamente ele cruzou novos limites. Aos dezesseis anos, ele estava testando todos os limites que conseguia encontrar. Rebelde, cabeça dura, uma tempestade ambulante de atitude e desafio.
Eu me lembrei dele voltando da escola, jogando a mochila no chão com um certo sorriso que eu não reconheci. “Eu estava pensando em ir para a casa da vovó neste verão”, ele disse. “Quer dizer, você sempre diz que ela poderia usar mais companhia. Eu poderia ficar de olho nela.”

Um adolescente sorridente | Fonte: Pexels
Minha primeira reação foi surpresa e um pouco de orgulho. Talvez ele estivesse virando uma nova página, se tornando responsável. Mas olhando para trás agora, enquanto eu acelerava pela rodovia escura, suas palavras me incomodavam de uma forma que não tinham incomodado antes.
Pisquei surpreso. “Você… quer ficar com a vovó? Você geralmente não vê a hora de sair de lá.”

Uma mulher chocada | Fonte: Pexels
“Eu ajudo a cuidar dela”, ele disse. “Você pode até deixar a cuidadora ir, mãe. Economizar algum dinheiro, sabia?”
Quanto mais eu dirigia, mais pedaços de nossas conversas recentes se encaixavam na minha mente, formando uma imagem da qual eu não gostava.
“As pessoas mudam”, ele deu de ombros com um sorriso estranho. Então ele olhou para mim com um meio sorriso. “Quer dizer, eu sou quase um homem agora, certo?”

Um adolescente sorridente com um telefone | Fonte: Pexels
Eu ignorei isso então, pensando que talvez ele estivesse finalmente crescendo. Mas agora, aquele sorriso parecia… estranho. Não caloroso ou genuíno, mas como se ele estivesse interpretando um papel.
Enquanto dirigia, lembrei-me de outros detalhes, coisas que eu tinha descartado na época. Uma semana depois de sua estadia, liguei, querendo saber da minha mãe diretamente. Ele atendia, alegre, mas rápido demais, como se estivesse direcionando a ligação. “Ei, mãe! A vovó está dormindo. Ela disse que está cansada demais para conversar hoje à noite, mas vou dizer a ela que você ligou.”

Uma mulher preocupada em seu telefone | Fonte: Freepik
Por que não me esforcei mais?
Minha mente correu de volta para como tudo começou. Éramos só nós dois desde que seu pai foi embora quando ele tinha dois anos. Eu tentei dar a ele o que ele precisava para permanecer com os pés no chão. Mas desde que ele chegou à adolescência, as pequenas rachaduras começaram a aumentar.

Um adolescente irritado | Fonte: Freepik
A única pessoa que parecia conseguir falar com ele de vez em quando era minha mãe. Ela tinha um jeito de desarmá-lo, embora até ela admitisse que ele estava “testando sua paciência”.
Disquei o número da minha mãe novamente, desejando que ela atendesse. Meu polegar batia na tela ansiosamente, mas ainda assim, nada.
O céu escureceu enquanto as casas se tornavam escassas, seu bairro rural logo à frente. A cada milha, minha mente repetia suas desculpas muito suaves, seu ato charmoso.

Uma mulher ao telefone no carro | Fonte: Freepik
Quando cheguei na casa da minha mãe, um arrepio percorreu meu corpo. Eu podia ouvir música tocando a dois quarteirões de distância. O gramado dela, antes tão arrumado, agora estava coberto de mato, ervas daninhas se emaranhando nos degraus da varanda. As venezianas estavam com tinta descascada e as luzes estavam apagadas, como se ninguém tivesse estado em casa nas últimas semanas.
Saí do carro, sentindo a descrença se transformar em uma raiva doentia. Garrafas de cerveja e latas de refrigerante amassadas estavam espalhadas pela varanda. Eu conseguia até sentir o cheiro de fumaça de cigarro saindo pela janela aberta.
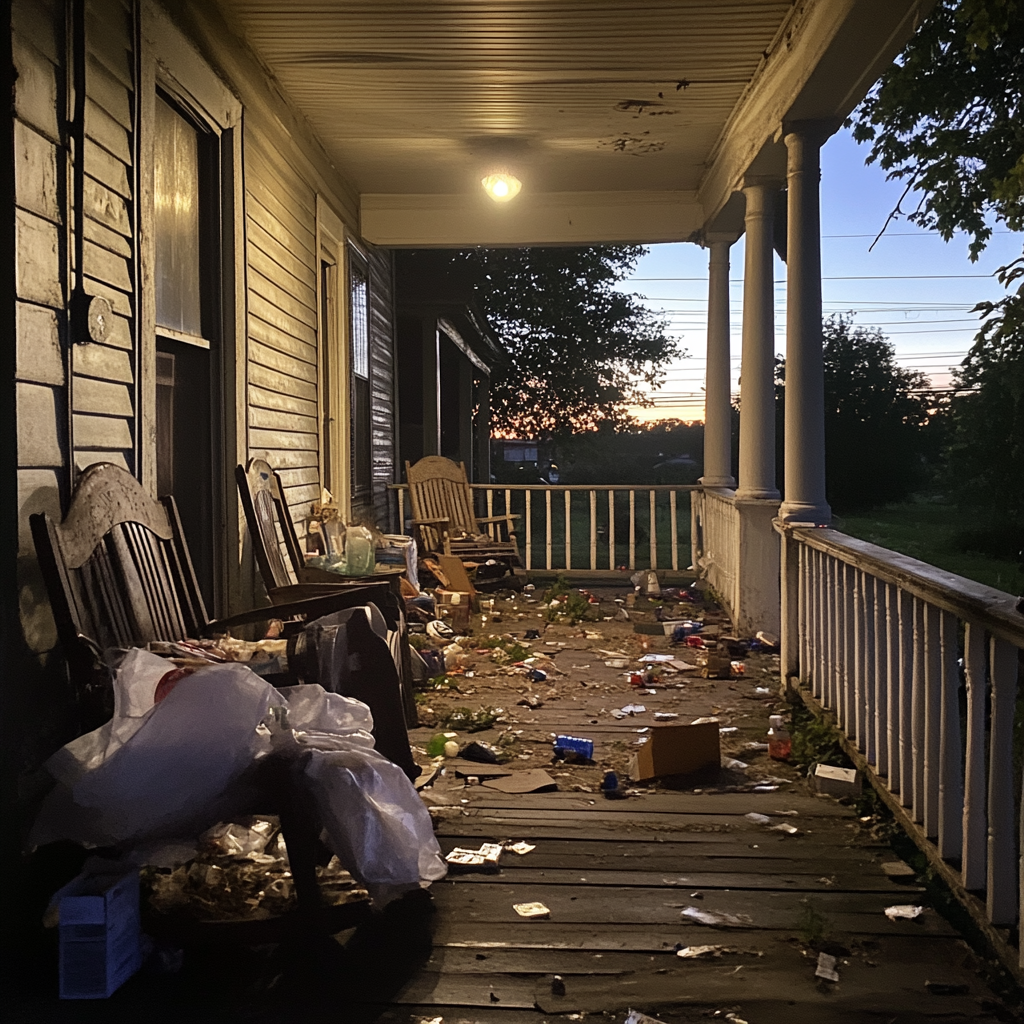

Uma varanda cheia de lixo | Fonte: Midjourney
Minhas mãos tremiam quando alcancei a porta e a abri.
E ali, bem na minha frente, estava o caos.
Estranhos enchiam a sala de estar rindo, bebendo, gritando por cima da música. Metade deles parecia ter idade para ser universitário, outros mal pareciam ter saído do ensino médio. Meu coração se contorceu, uma mistura de fúria e mágoa me inundando.

Uma mulher furiosa | Fonte: Pexels
“Onde ele está?”, sussurrei, examinando a multidão, a descrença dando lugar a uma raiva concentrada. Eu empurrei as pessoas, chamando seu nome. “Com licença! Saiam!”
Uma garota esparramada no sofá olhou para mim, piscando preguiçosamente. “Ei, moça, relaxa. Estamos só nos divertindo”, ela falou arrastado, acenando uma garrafa na minha direção.
“Onde está minha mãe?”, perguntei bruscamente, mal conseguindo conter o tom áspero da minha voz.

Uma mulher gritando | Fonte: Pexels
A garota apenas deu de ombros, despreocupada. “Não sei. Não vi nenhuma senhora aqui.”
Ignorando-a, continuei pela sala lotada, gritando o nome do meu filho por cima da música alta. Olhei de rosto em rosto, meu coração batendo mais rápido a cada passo. Cada segundo que passava fazia a casa parecer mais com a de um estranho, mais como um lugar que minha mãe nunca permitiria, muito menos morar.
Adolescentes festejando | Fonte: Pexels
“Mãe!”, chamei, minha voz desesperada quando cheguei ao fim do corredor, perto da porta do quarto dela. Estava fechada, a maçaneta levemente arranhada, como se tivesse sido aberta e fechada uma centena de vezes só na última hora.
Bati forte, com o coração acelerado. “Mãe? Você está aí? Sou eu!”
Uma voz fraca e trêmula respondeu, quase inaudível sobre o barulho. “Estou aqui. Por favor, apenas me tire daqui.”

Uma mulher batendo freneticamente na porta fechada | Fonte: Midjourney
Senti uma onda de alívio e horror enquanto me atrapalhava com a maçaneta e abria a porta. Lá estava ela, sentada na cama, o rosto pálido e abatido, os olhos marejados de exaustão. O cabelo dela estava desgrenhado, e eu podia ver olheiras sob seus olhos.
“Ah, mãe…” Atravessei a sala num piscar de olhos, caindo de joelhos ao lado dela e envolvendo meus braços ao redor dela.

Uma senhora idosa cobrindo os ouvidos | Fonte: Freepik
A mão dela, frágil mas firme, agarrou a minha. “Ele começou com apenas alguns amigos”, ela murmurou, sua voz quase um sussurro. “Mas quando eu disse para ele parar, ele ficou bravo. Ele… ele disse que eu estava apenas atrapalhando.” A voz dela vacilou. “Ele começou a me trancar aqui. Disse que eu estava… estragando a diversão dele.”
Uma onda nauseante de raiva surgiu em mim. Eu tinha sido cego, tolo o suficiente para acreditar na promessa do meu filho de “ajudar”. Respirei fundo, acariciando sua mão. “Eu vou consertar isso, mãe. Eu juro.”

Uma senhora idosa em seu quarto | Fonte: Freepik
Ela assentiu, segurando minha mão, seus próprios dedos frios e trêmulos. “Você tem que fazer isso.”
Voltei para a sala de estar, meu maxilar tão apertado que doía. E lá estava meu filho, encostado na parede, rindo com um grupo de crianças mais velhas.
Quando ele olhou para cima e me viu, seu rosto ficou pálido.
“Mãe? O que… o que você está fazendo aqui?”

Um adolescente chocado | Fonte: Freepik
“O que estou fazendo aqui?”, ecoei, minha voz firme com uma calma que eu não sentia. “O que você está fazendo aqui? Olhe ao redor! Olhe o que você fez com a casa da sua avó!”
Ele deu de ombros, tentando parecer tranquilo, mas eu vi sua máscara escorregando. “É só uma festa. Você não precisa surtar.”
“Tirem todos daqui. Agora.” Minha voz era de aço, e dessa vez, cortou o barulho. A sala inteira pareceu congelar. “Vou chamar a polícia se esta casa não estiver vazia nos próximos dois minutos.”

Uma mulher furiosa | Fonte: Freepik
Um por um, os festeiros saíram, murmurando e tropeçando em direção à porta. A casa esvaziou, deixando apenas móveis quebrados, garrafas vazias e meu filho, que agora estava sozinho nos destroços que ele havia feito.
Quando o último convidado foi embora, eu me virei para ele. “Eu confiei em você. Sua avó confiou em você. E é assim que você a retribui? Era assim que você achava que ‘ajudar’ parecia?”
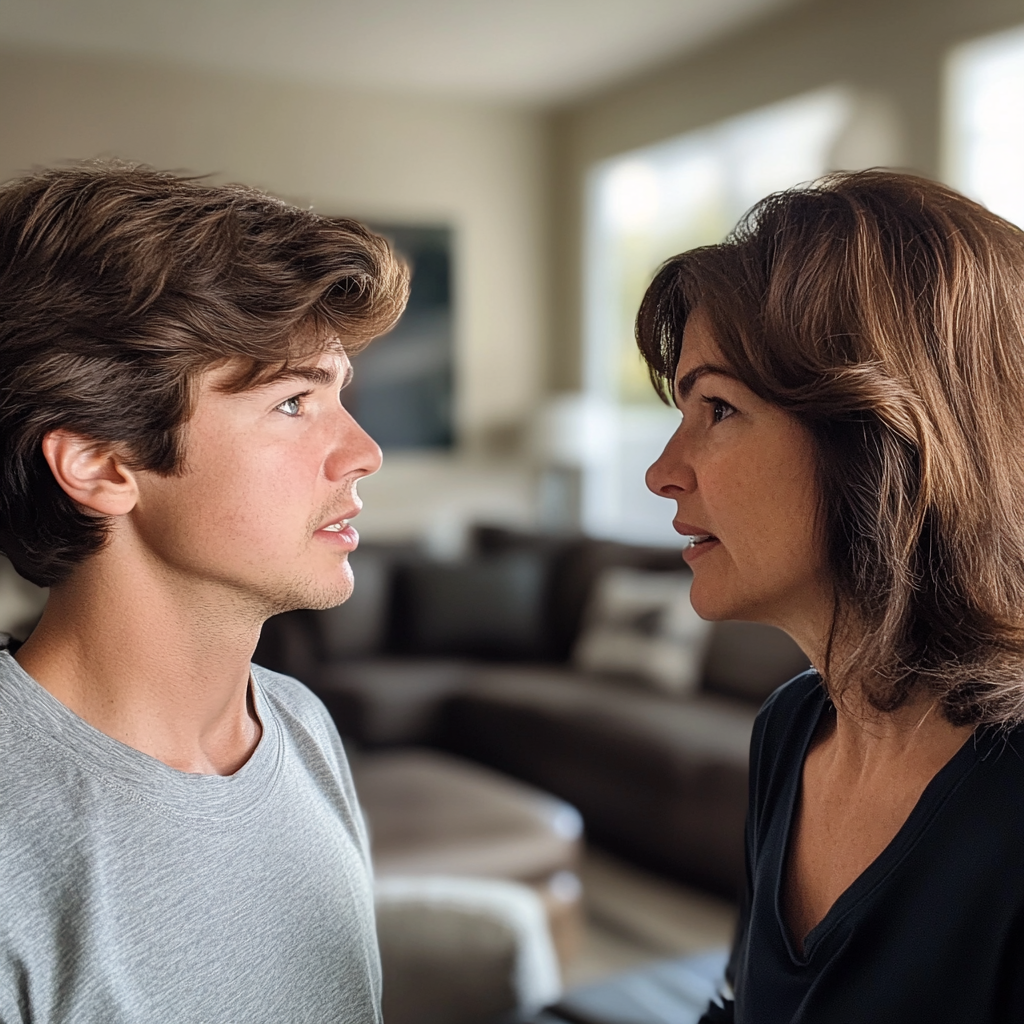

Uma mulher confrontando seu filho | Fonte: Midjourney
Ele deu de ombros, um sorriso defensivo torcendo seu rosto. “Ela não precisava de espaço. Você está sempre no meu pé, mãe. Eu só queria um pouco de liberdade!”
“Liberdade?” Minha voz tremeu de descrença. “Você vai aprender o que é responsabilidade.” Respirei fundo, sentindo o peso de cada palavra. “Você vai para um acampamento de verão com regras rígidas, e eu estou vendendo seus eletrônicos, tudo que é valioso, para pagar pelos danos. Você não ganha uma única ‘liberdade’ até conquistá-la.”
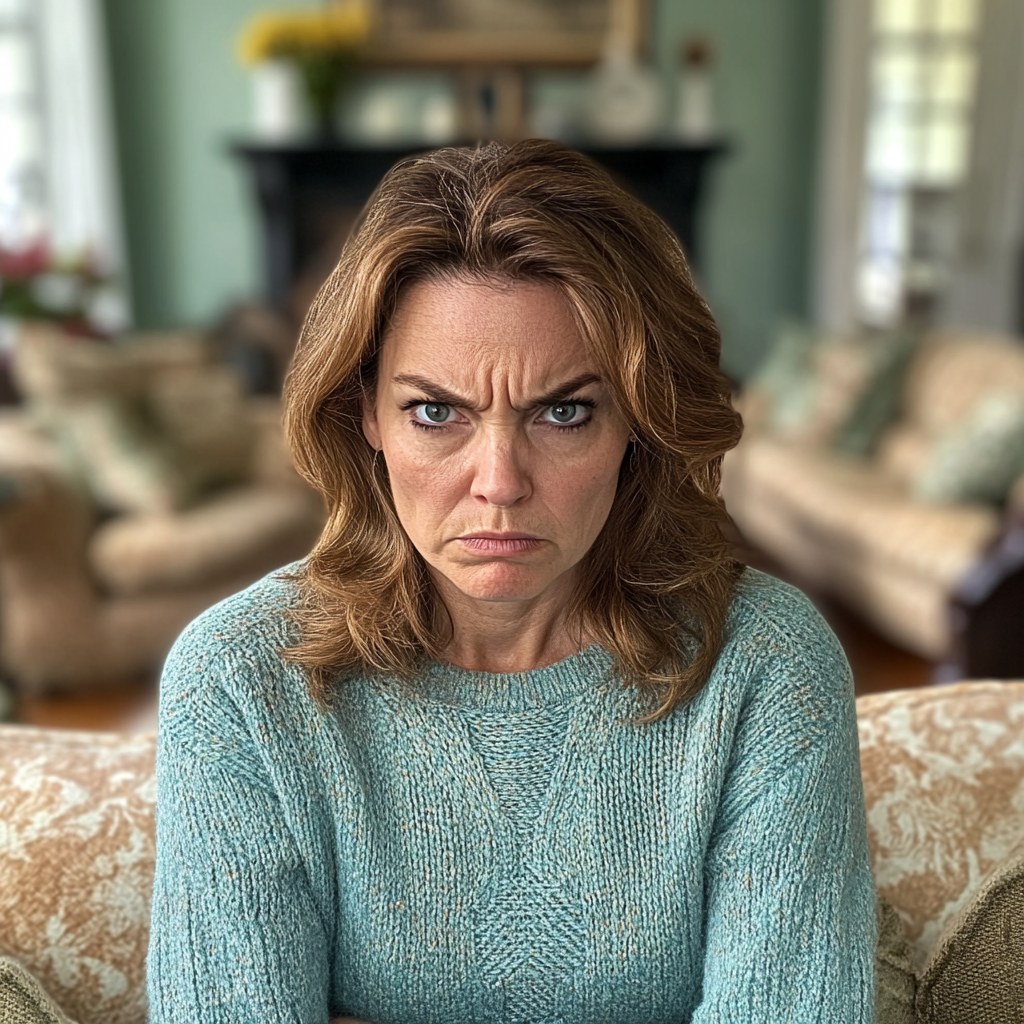

Uma mulher furiosa em sua sala de estar | Fonte: Midjourney
“O quê?” Sua bravata vacilou, o medo cintilou em seus olhos. “Você não pode estar falando sério.”
“Oh, eu sou”, eu disse, a voz mais fria do que eu já tinha ouvido. “E se você não mudar, você estará fora de casa quando fizer dezoito anos. Eu cansei de desculpas.”
No dia seguinte, eu o mandei para o acampamento. Seus protestos, sua raiva, tudo desapareceu conforme o verão passou, e pela primeira vez, ele foi forçado a encarar as consequências.

Um adolescente em um acampamento | Fonte: Pexels
Enquanto eu consertava a casa da minha mãe naquele verão, senti os pedaços da nossa família começarem a se consertar. Pouco a pouco, cômodo por cômodo, limpei os cacos de vidro, remendei as paredes e mantive a esperança de que meu filho voltaria para casa uma pessoa diferente.
Depois daquele verão, vi meu filho começar a mudar. Ele ficou mais quieto, mais estável, passando as noites estudando em vez de desaparecer com os amigos.
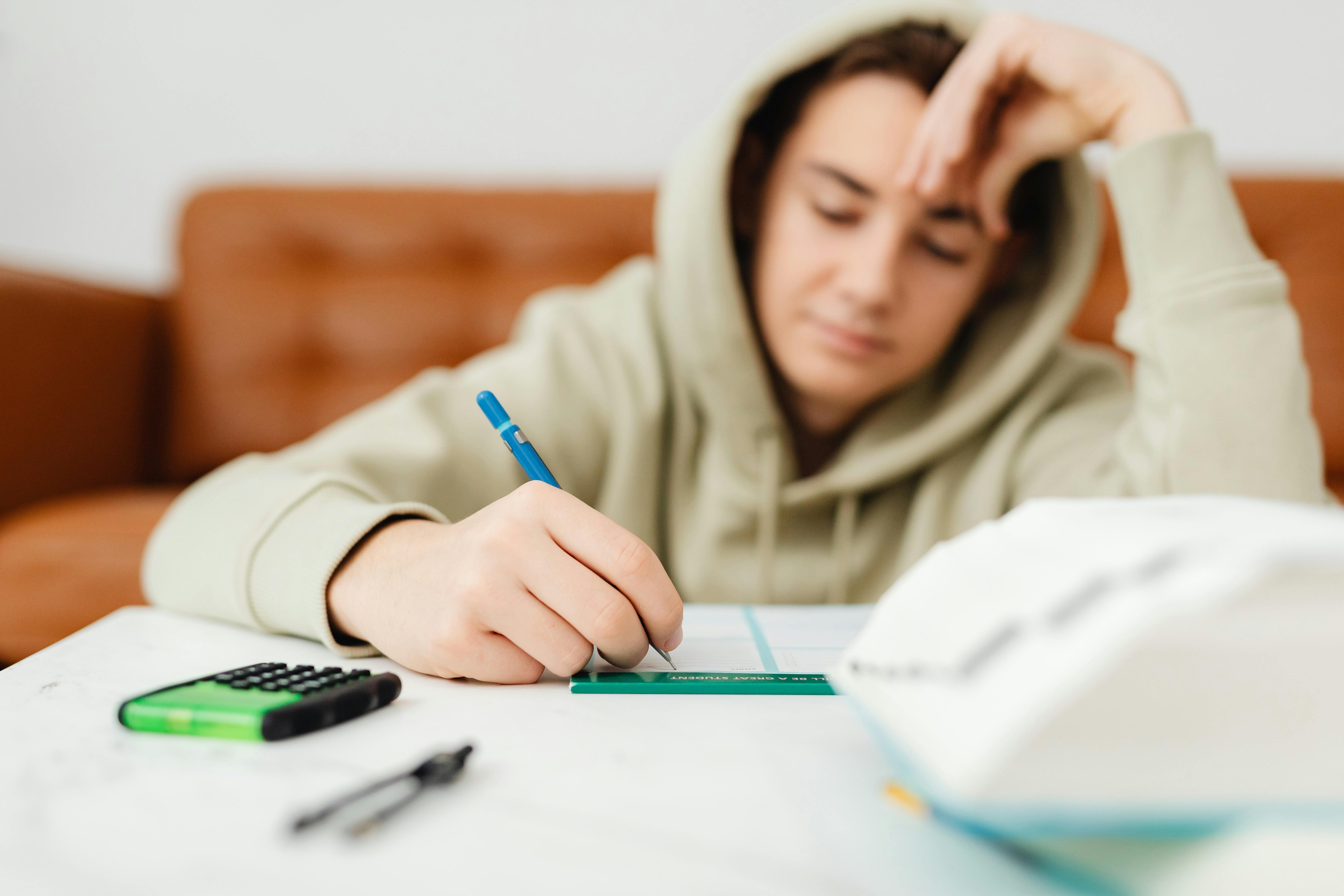

Um menino fazendo sua lição de casa | Fonte: Pexels
Pequenos atos como ajudar em casa e pedir desculpas sem ser solicitado se tornaram rotina. A cada dia, ele parecia mais consciente e mais respeitoso, como se finalmente estivesse se tornando o homem que eu esperava.
Dois anos depois, eu o vi subir os degraus da minha mãe novamente, de cabeça baixa. Ele estava prestes a se formar com honras e se matricular em uma boa faculdade. Em sua mão estava um buquê, seu olhar sincero e suave de uma forma que eu nunca tinha visto.
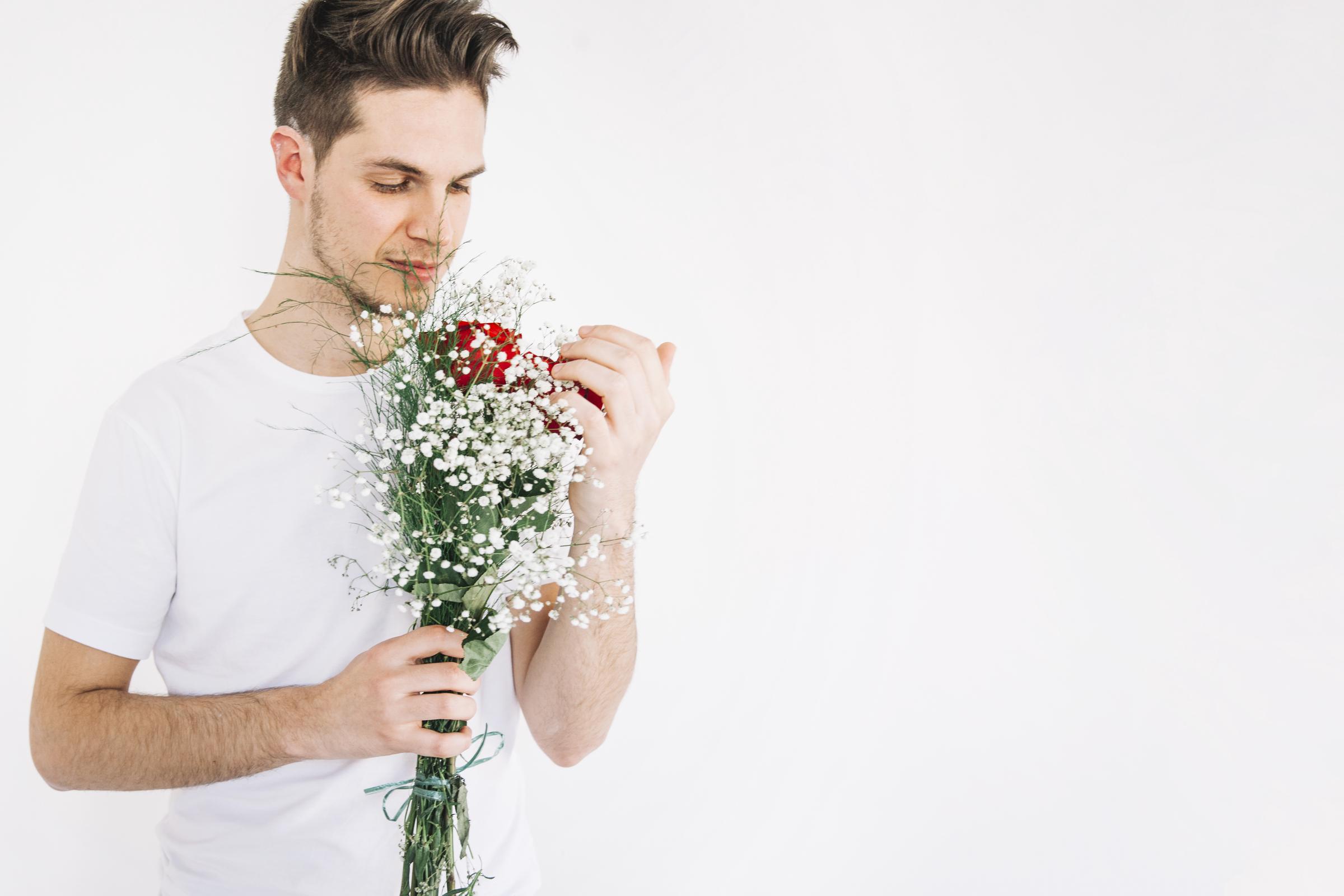

Um jovem com flores | Fonte: Freepik
“Sinto muito, vovó”, ele disse, sua voz grossa de arrependimento. Prendi a respiração, observando enquanto o garoto que eu tinha lutado para criar oferecia a ela um pedaço de seu coração.
Gostou desta história? Considere conferir esta : Quando a nova esposa do meu pai me expulsou do meu quarto e me jogou no galpão, pensei que tinha chegado ao fundo do poço. Mas a visita surpresa da mamãe e a revelação chocante sobre a casa viraram tudo de cabeça para baixo, me deixando imaginando se eu me sentiria em casa com o papai novamente.
Este trabalho é inspirado em eventos e pessoas reais, mas foi ficcionalizado para fins criativos. Nomes, personagens e detalhes foram alterados para proteger a privacidade e melhorar a narrativa. Qualquer semelhança com pessoas reais, vivas ou mortas, ou eventos reais é mera coincidência e não intencional do autor.
O autor e a editora não fazem nenhuma reivindicação quanto à precisão dos eventos ou à representação dos personagens e não são responsáveis por nenhuma interpretação errônea. Esta história é fornecida “como está”, e quaisquer opiniões expressas são as dos personagens e não refletem as opiniões do autor ou da editora.



Leave a Reply