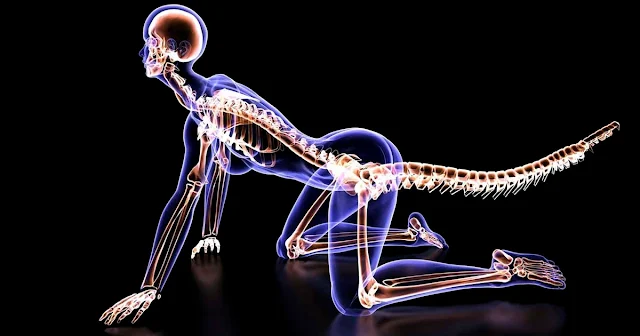
One of the most remarkable changes in human evolution is the loss of our tails, a transformation that occurred around 25 million years ago. This pivotal shift not only altered the trajectory of our species but also marked a significant moment in the evolutionary history of primates. While scientists have long speculated on why humans lost their tails, the genetic cause has remained elusive—until now. A recent study published in Nature has finally uncovered the genetic factors responsible for this evolutionary change.
The Quest to Understand Tail Loss
The journey to unravel the mystery of human tail loss began in an unexpected way. Bo Xia, a graduate student at New York University, was inspired to investigate the origins of the human tailbone after injuring his own coccyx. This personal curiosity led Xia and his team to embark on a groundbreaking scientific investigation.
Through careful research, the team focused on the TBXT gene, which plays a crucial role in regulating tail length in various species. Their research revealed a unique genetic mutation within this gene, providing a major breakthrough in understanding human evolution.
The Role of Jumping Genes
A key aspect of this discovery lies in the role of Alu elements, often called “jumping genes.” These genetic elements, specific to primates, can move within the genome and cause significant changes. The researchers found that Alu elements inserted themselves into the TBXT gene, triggering a chain reaction that led to the loss of our tails.
This insertion activated a process known as alternative splicing, where RNA molecules are cut and restructured, which ultimately led to the deletion of a crucial exon. This change altered the structure and function of the resulting protein, leading to the tail loss seen in humans.
Validation Through Mice Studies
To confirm their findings, the researchers engineered laboratory mice with the same genetic mutations found in humans and apes. These genetically altered mice lost their tails, providing compelling evidence that the identified mutation plays a crucial role in the absence of tails in humans and other primates.
However, the study also uncovered a downside to tail loss: an increased risk of neural tube defects, such as spina bifida. This finding highlights the complex balance between evolutionary benefits and potential genetic trade-offs.
The Broader Implications
This discovery has profound implications not just for understanding human evolution, but also for human anatomy and health. The loss of our tails was not a random event but a genetic adaptation with lasting consequences. It illustrates the complex relationship between genetic changes and the way they shape our physiology over time.
As we continue to study our evolutionary past, these findings remind us of the intricate process of natural selection and genetic innovation that has shaped humanity. This breakthrough also underscores the power of scientific inquiry in uncovering the mysteries of our origins, offering insight into the past that can help us understand our future.
The identification of the genetic reasons behind tail loss is a testament to the persistence of scientific exploration and the ongoing quest for knowledge about our evolutionary journey.
Before his death, Matthew Perry revealed the truth about Jennifer Aniston

Actor Matthew Perry, who passed away, made millions of people happy throughout the world with his legendary performance as Chandler Bing. Regretfully, despite his ability to make others laugh, he struggled with addiction for years and was unable to assist himself.
Perry published his memoir Friends, Lovers, and the Big Terrible Thing last year, in which he candidly discussed his struggle with addiction. He also disclosed some information regarding co-star Jennifer Aniston among the others.
Over the weekend, Perry’s LA home’s hot tub was discovered to be unresponsive. His death’s precise cause is still under investigation.
The actor, who was born in 1969 to an American father and a Canadian mother, debuted in a movie in 1988 called A Night in the Life of Jimmy Reardon, which also starred the late River Phoenix.
He also starred in Beverly Hills, 90210, and Growing Pains, Sydney, costarring Valerie Bertinelli.
His breakthrough performance came in Friends as the sardonic Chandler Bing. He spent ten years in the job, from 1994 to 2004.

Throughout the course of his multi-decade career, Perry starred alongside Salma Hayek in the 1997 romantic comedy Fools Rush In. He also costarred with Bruce Willis in the 2000 film The Whole Nine Yards and the 2004 follow-up The Whole Ten Yards.
Perry became well-known after landing a role in Friends, one of the most watched television programs ever. But he also began misusing alcohol at that same period.
Kind of, I could manage it. However, I was deeply involved in a lot of trouble by the time I was 34,” Perry acknowledged. However, I did spend some years sober throughout that period. The year I stayed sober the entire time was Season 9. And you know for which season I received a best actor nomination? That ought to tell me something, I thought.

He experienced a health crisis in 2018 after being admitted to the hospital for a stomach perforation. He spent two weeks in a coma and five months overall.
Perry told People, “The doctors told my family that I had a two percent chance to live.” “I was placed on an ECMO machine, which does all of your heart and lung breathing. That is referred to be a Hail Mary. Nobody makes it out of that.
Perry often acknowledged that the other members of the Friends cast knew about his addiction and supported him because they were close in real life as well as on television.
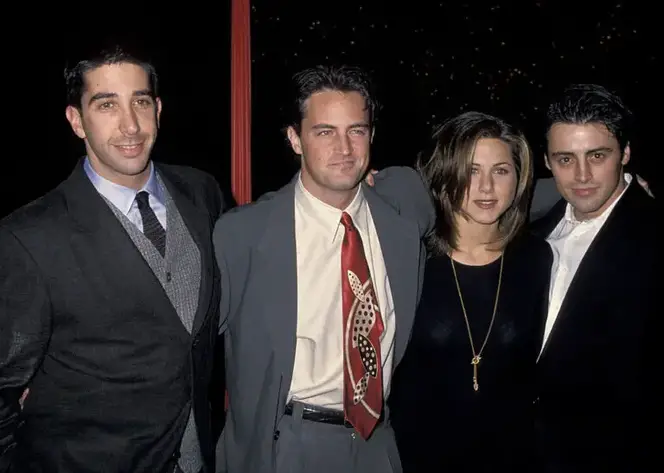

They were really patient and understanding. It resembles penguins. In the wild, penguins tend to support and embrace each other when one becomes ill or severely injured. Until that penguin can walk on its own, they circumambulate it. For me, the actors kind of did that, according to Perry.
But through thick and thin, Jennifer Aniston was the one who was at his side. It was she who kept in constant touch with him through his highs and lows.
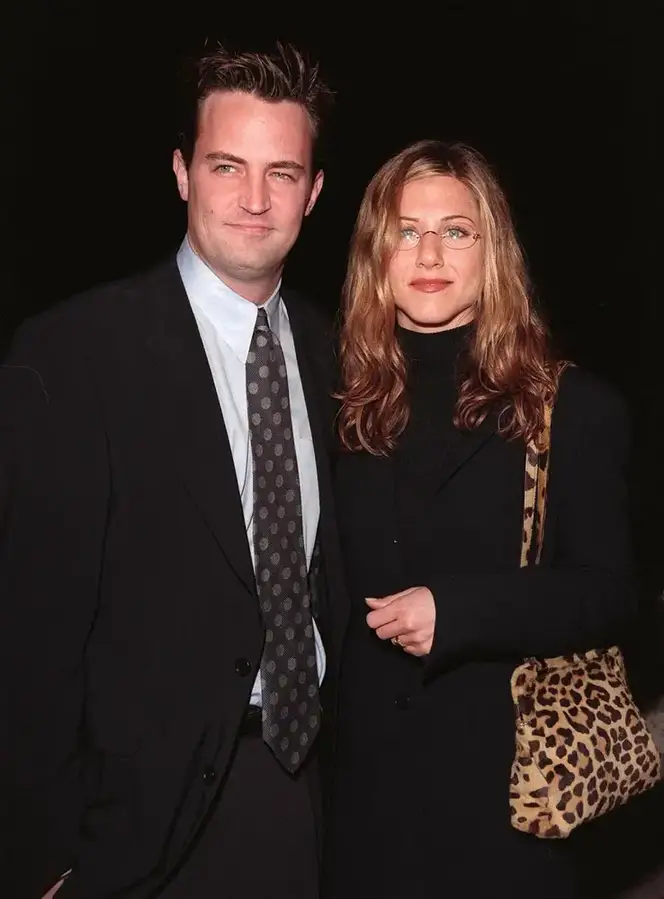

He stated, “She was the one that reached out the most,” in an interview with Diane Sawyer from October 2022. “You know, she has my sincere gratitude for that.”
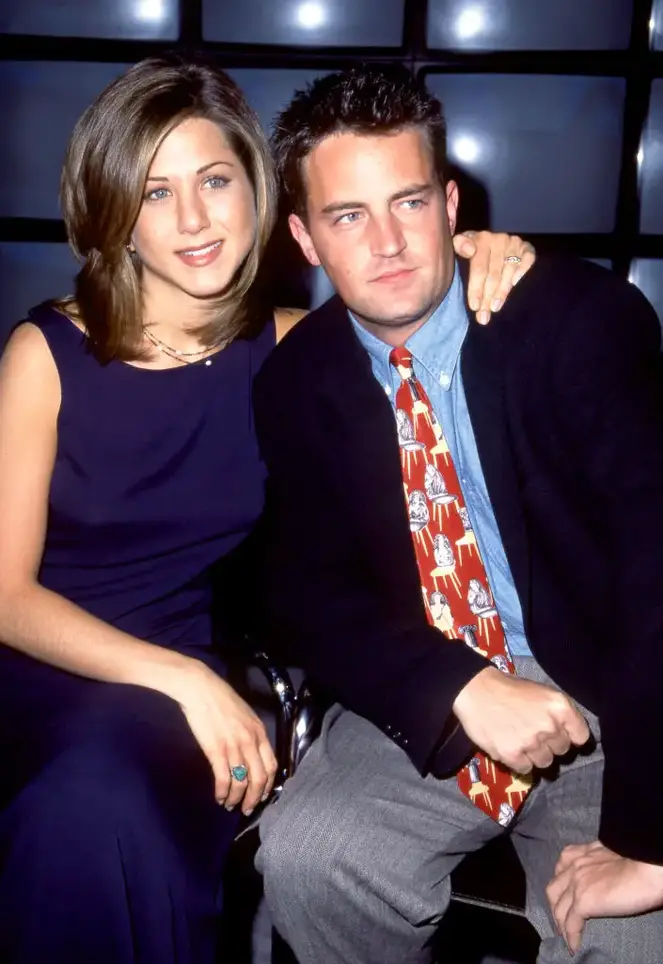
Simultaneously, Aniston was the first to confront him over his drinking issues.
Sawyer mentioned a surprise in Perry’s book when he remarked, “Jennifer, she says, ‘We know you’re drinking.’”
Perry answered, “Yeah, imagine how scary a moment that was.”
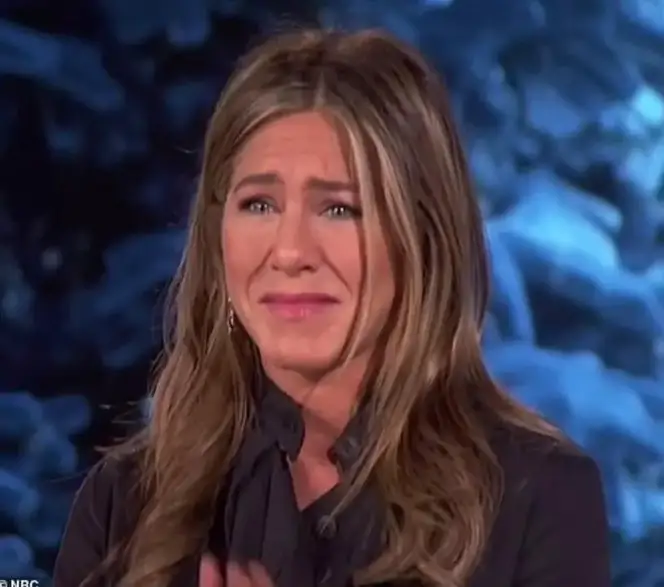


As a friend and actor, Matthew made the world a much happier place. They wrote in their statement, “You all meant so much to him and we appreciate the incredible outpouring of love.
The late actor received tributes from admirers, coworkers, producers, and other celebrities.



Leave a Reply