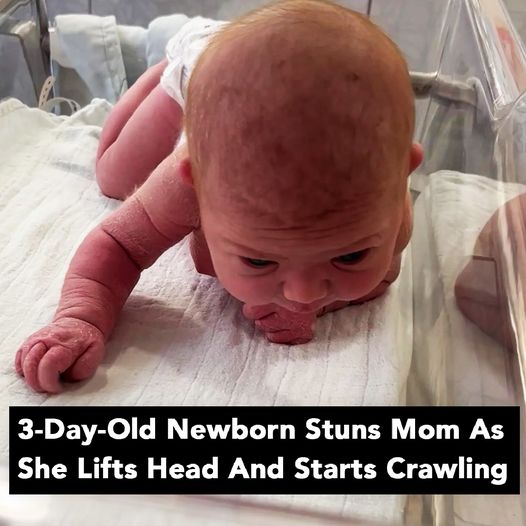
Three weeks past her due date, Nyilah Daise Tzabari made her grand entrance into the world with an eagerness to make up for lost time. At just three days old, she stunned her parents by lifting her head and crawling across her hospital cot.
Nyilah’s extraordinary strength left her first-time parents, Samantha Mitchell and Ofer Tzabari, in awe. Still in the hospital, the couple managed to capture the moment on video, showing their daughter doing things typically seen in much older babies.
“The video was taken when Nyilah wasn’t even a full three days old—she was only two and a half days old,” Samantha shared. A 34-year-old mother from White Oak, PA, Samantha was amazed, saying that despite her two decades of experience with children, she had never seen anything like it. “I’ve never had a newborn like this,” she added.
In the viral TikTok video, which has now garnered over 57.5 million views, baby Nyilah uses her tiny arms to prop herself up and crawl. In the background, you can hear Samantha’s mother exclaiming in disbelief, while Samantha herself is equally astonished, saying, “Oh my gosh. Mom! She’s crawling! How does that even move?”
Nyilah was born on February 27, 2023, weighing 7 lbs 6 oz. Samantha, who initially recorded the video to show family and friends, said, “If I didn’t get it on film, no one would have believed me, not even my fiancé, Ofer.” The video captures the exact moment Samantha witnessed her baby crawl for the first time, leaving her in complete shock.
Fans on TikTok were just as amazed, with many joking that “these new babies are different—they come out crawling and walking at one month old.” Others chimed in with lighthearted comments, saying, “Rumor has it she left on a plane the next day to live her life.”
According to Healthline, most babies start to crawl between six to 12 months, but Nyilah is clearly on a fast track. In fact, her quick development has continued since that viral moment. At 18 days old, she was already rolling from her belly to her back. By one month, she was smiling at her mom, and by two months, she was rolling from her back to her belly. At three months, she was even showing off her strength by playfully punching her mom in the face during a video.
Nyilah’s rapid growth hasn’t stopped there. She is already standing with support, and Samantha is confident that walking is just around the corner. “She puts so much weight on her legs and refuses to buckle her knees,” Samantha shared, adding that Nyilah no longer even needs her head and neck supported.
“She’s a very alert baby, and her strength has surprised us from day one,” Samantha said. At seven weeks, Nyilah began babbling and mimicking words spoken by her parents, even trying to say, “I love you.” She loves making noises to get a reaction, showcasing her playful and clever personality.
Nyilah is not just strong but also incredibly happy. “She smiles and laughs all the time,” Samantha said. “The second you smile at her, she lights up and smiles right back.”
For Samantha and Ofer, their daughter’s actions have been a pleasant surprise. “I thought this was normal for newborns, but it turns out Nyilah’s behavior is far from typical,” Samantha explained.
As Nyilah continues to grow and amaze, her family is preparing for even more milestones. With her rapid development, the future is sure to be filled with excitement. Samantha and Ofer’s “super baby” is already taking the world by storm, and we can’t wait to see what she does next! Congratulations to the happy family!
6 year old girl sings the hall are stunned Watched in 1 day 90․000000 million people

That’s wonderful! Singing can be such a joyful and expressive activity for people of all ages.
It’s great to hear about young talents exploring their voices and sharing their music.
If you have any specific questions or if there’s anything else you’d like to know or discuss about children singing, feel free to ask!



Leave a Reply