Ever wondered just how much data your brain can hold? We often compare the brain to a supercomputer, but what if that comparison isn’t just a metaphor—it’s literal? Deep within your brain, at the junctions where neurons meet, lies an extraordinary form of biological storage: the synapse. And thanks to breakthroughs in information theory, we’re beginning to quantify its staggering capacity.
In this article, we’ll dive into how synaptic storage works, how scientists measure it, and why this knowledge could shape the future of data storage—from artificial intelligence to DNA-based memory.
What Are Synapses and Why Are They Important?
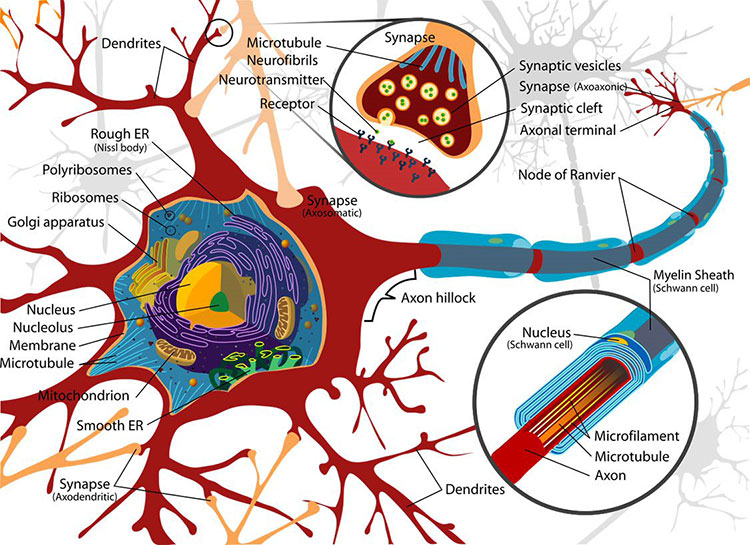
Think of neurons as the brain’s messengers. But without synapses—the gaps between them where signals are transmitted—those messages would go nowhere. A synapse is where the magic happens: it’s the space where one neuron sends a chemical or electrical signal to another, sparking thoughts, memories, movements, and more.
Now here’s the kicker: each of these tiny junctions doesn’t just pass along data—it stores it.
Your brain has about 86 billion neurons, and each one can form around 1,000 synapses. That’s a total of roughly 125 trillion synapses buzzing away in your brain, constantly sending and receiving signals. These connections form the foundation of your memories, knowledge, and perception.
Measuring Synaptic Storage with Information Theory
To understand how synapses store information, scientists turn to information theory—a branch of mathematics that deals with encoding, decoding, and compressing data. Think of it like analyzing how much a hard drive can hold, but on a biological scale.
Video : 2-Minute Neuroscience: Synaptic Transmission
Each synapse, as it turns out, can store up to 4.7 bits of information. That might not sound like much until you consider the scale:
- 1 bit is a single piece of binary data (a 0 or 1)
- 4.7 bits per synapse × 125 trillion synapses = over 500 trillion bits of potential storage
Translated into digital terms, your brain can theoretically store more data than the entire internet—all in a compact, low-energy package powered by biology.
The Brain’s Efficiency: Powering Trillions of Connections
Here’s something even more mind-blowing: while your laptop heats up and guzzles electricity, your brain handles all of this complex storage and processing using roughly 20 watts of power—that’s about the same as a dim light bulb.
This insane efficiency is what’s inspiring researchers to build neural networks and deep learning systems that mimic the brain. If computers could process and store data like synapses do, we’d have faster, smarter, and greener technology.
Artificial Intelligence and Synaptic Models
The field of AI, especially machine learning and deep learning, borrows heavily from how the brain processes and stores information. Artificial neural networks use layers of interconnected nodes (inspired by neurons) to simulate learning.
But here’s where it gets interesting: researchers are now using real data about synaptic information capacity to refine these systems. The goal? To build AI models that are more human-like, not just in intelligence but in efficiency and adaptability.
Imagine a future where your smartphone thinks and stores information with the same elegance as your brain. That future isn’t science fiction—it’s science.
Beyond the Brain: DNA as the Ultimate Storage Device
While the brain remains the pinnacle of biological storage, it’s not the only game in town. Enter DNA, nature’s original information vault.
DNA doesn’t just code for life—it can be used to store digital data. And we’re not talking small files here. A single gram of DNA can hold up to 215 petabytes of data. That’s 215 million gigabytes—enough to store every photo, song, and document you’ve ever owned, plus millions more.
In fact, researchers have already done it. In one groundbreaking study, scientists encoded a 52,000-word book into synthetic DNA. They converted the digital content into binary (0s and 1s), then translated those digits into DNA’s four-letter alphabet: A, T, G, and C. The result? A physical strand of DNA holding a complete, retrievable digital file.
Why DNA Storage Matters for the Future
Traditional storage devices—hard drives, SSDs, even cloud servers—have physical limits. They degrade over time and take up massive amounts of space. DNA, on the other hand, is incredibly compact, durable, and stable for thousands of years if stored properly.
If scaled correctly, DNA storage could revolutionize how we preserve knowledge. Imagine backing up the entire contents of the Library of Congress on something no bigger than a sugar cube. That’s the level we’re talking about.
Video : How Your Brain Remembers: Neurons & Synapses Explained!
Bridging Biology and Technology
What’s exciting is how these two areas—brain synapses and DNA storage—are starting to intersect. Both are nature’s proof that small-scale systems can handle mind-blowing amounts of data. As scientists continue to decode these systems using information theory, they’re finding ways to integrate them into technology.
It’s not about replacing computers with brains or turning DNA into a USB drive. It’s about learning from nature’s most efficient designs to build the next generation of computing and storage systems.
Conclusion: Reimagining Storage in a Biological World
Your brain’s 125 trillion synapses silently store and process more information than entire server farms, all while sipping on 20 watts of energy. Meanwhile, DNA—the code of life—is showing us how to pack massive libraries of data into microscopic strands.
By measuring synaptic storage capacity with information theory, we’re not just understanding the brain better—we’re laying the foundation for a new era of intelligent, efficient technology.
The takeaway? Nature has already solved problems we’re only beginning to understand. And the more we study it, the closer we get to unlocking the true potential of both our minds and our machines.
Sharpen Your Mind with This Simple Challenge

Have you ever wondered about the true potential of your mind? Our brain is an incredible tool, capable of performing complex tasks and calculations. Yet, we often rely on calculators or external devices for simple math problems. This article introduces a fascinating puzzle that challenges you to rely solely on your mental abilities to solve it. The PuzzleThe challenge is simple but can easily trip up even seasoned problem-solvers. It goes as follows:Start with 1000. Add 40.Add 1000.Add 30. Add another 1000.Add 20.Add a final 1000. Add 10.Most people rush through it, mentally tallying numbers and assuming the total comes to 5000. In fact, the true result is 4100. This discrepancy is due to the way our brain processes the information quickly, often skipping over smaller details. Let’s break down how to solve it step by step to avoid the common mistake. Breaking Down the CalculationLet’s calculate it slowly and deliberately to avoid any confusion: Starting point: 1000Add 40: 1000 + 40 = 1040Add 1000: 1040 + 1000 = 2040 Add 30: 2040 + 30 = 2070Add another 1000: 2070 + 1000 = 3070Add 20: 3070 + 20 = 3090 Add a final 1000: 3090 + 1000 = 4090Finally, add 10: 4090 + 10 = 4100The correct answer is 4100. Simple, right? But why do so many people make the mistake of thinking it’s 5000? Why Our Brain is TrickedThis puzzle is a perfect example of how our cognitive shortcuts can deceive us. When we perform rapid calculations, our brain tends to group numbers in a way that can lead to errors. In this case, the mind often registers the sum of all the 1000s (which would total 4000), and then quickly adds 40, 30, 20, and 10, but often ends up overshooting and arriving at 5000. The confusion occurs when the brain processes these smaller numbers too quickly, sometimes combining them incorrectly.This phenomenon is called cognitive overload. When we try to mentally juggle too much information at once, we start to rely on assumptions and shortcuts rather than precise calculations. The more numbers we add, the more our mind tries to simplify the process—and that’s where mistakes happen.Strengthening Your Mental MathNow that you understand how your brain can play tricks on you, it’s time to work on improving your mental math. The best way to avoid errors like this in the future is to break down calculations into smaller steps and double-check each stage of the process. Here are a few tips to sharpen your mental math skills: Visualize the Numbers: Instead of letting your brain rush through the sequence, try to visualize each step as if you’re writing it down. This can help you keep track of the running total and avoid miscalculations.Practice with Smaller Numbers: Start with smaller numbers and build your way up to more complex calculations. This trains your brain to handle larger sums with greater accuracy.Stay Calm: Cognitive overload often happens when we’re trying to solve problems too quickly. Take a deep breath, slow down, and approach the challenge with patience. Use Estimation: If you’re ever in a situation where precision isn’t critical, estimation can be a useful tool. But in cases like this puzzle, precision is key, so break down the numbers methodically.Practice Regularly: Mental math, like any other skill, improves with practice. Dedicate time to solving puzzles and problems like this one regularly, and you’ll soon notice an improvement in your accuracy.The Importance of Keeping Your Brain SharpJust like physical exercise keeps our bodies healthy, mental challenges keep our minds sharp. Engaging in puzzles like this one strengthens cognitive function, improves concentration, and enhances problem-solving abilities. Regularly challenging your brain with exercises like mental math can also reduce the risk of cognitive decline as you age.In a world where we often rely on technology to do the thinking for us, taking a few moments to solve problems mentally is a great way to reconnect with the power of your own mind. So, the next time you’re tempted to pull out your phone’s calculator, give your brain a chance to do the work instead.ConclusionThe mental math challenge presented in this article is more than just a simple exercise—it’s a reminder of the capabilities our minds possess. While it might be easy to reach for a calculator, solving problems like this one can help keep your brain sharp and engaged. If you found yourself tricked by the 5000-answer mistake, don’t worry—you’re not alone! Just remember, next time, to slow down, visualize, and approach the task one step at a time. You’ll not only get the right answer but also give your brain a healthy workout.



Leave a Reply